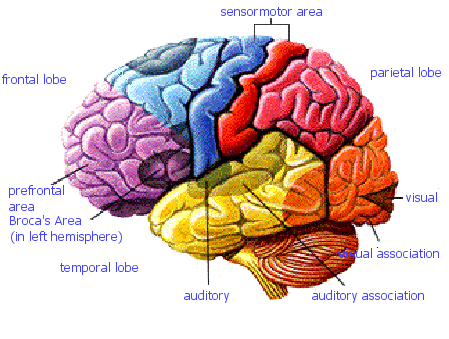
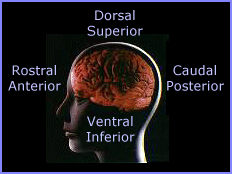
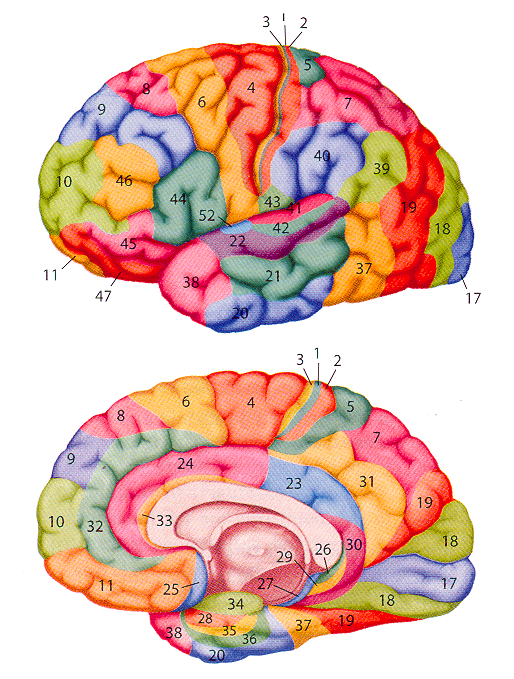
Jessica's neuroanatomy tutorial
(compiled by Jessica Grahn)
You can also use an interactive brain atlas.
|
If only the brain really did come in colours... |
Orientation descriptions
|
|
The AC / PC line
The line joining the Anterior Commissure (AC) and Posterior Commissure (PC)
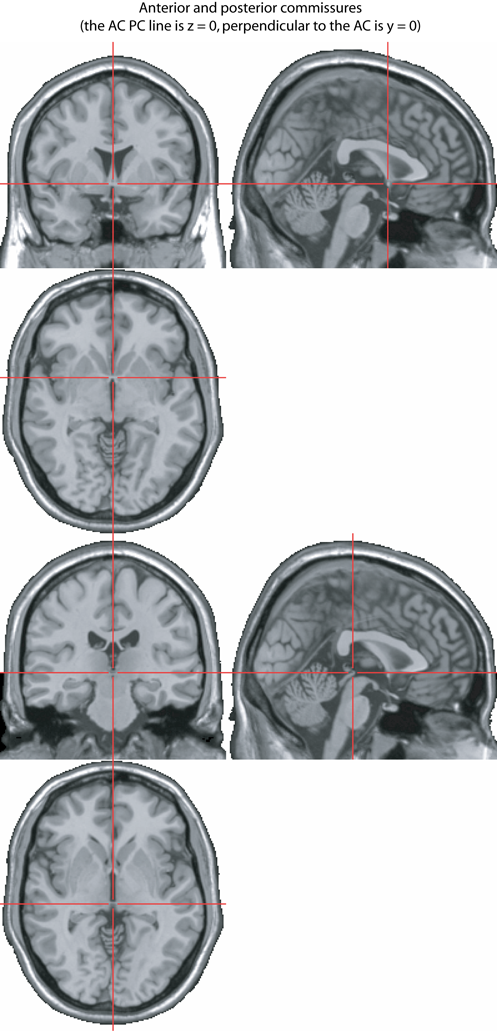
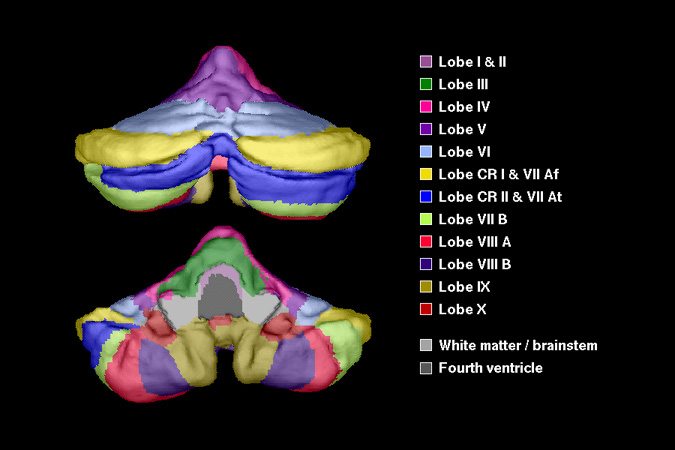
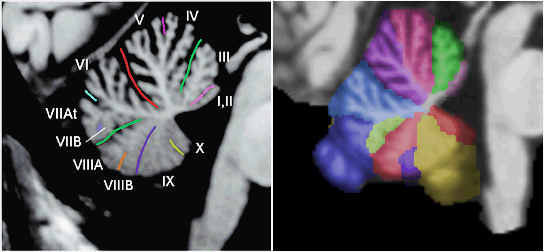
The Cerebellum
(Schmahmann, J.D., et al., Neuroimage, 1999, 10:233-260. )
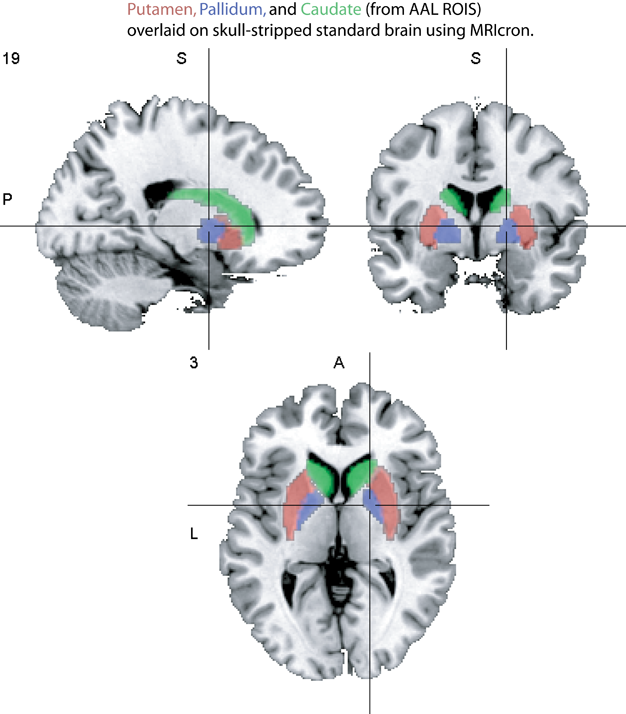
The Basal Ganglia
Caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus (also called pallidum by AAL template).
The caudate, putamen, and ventral striatum (the most ventral outline)
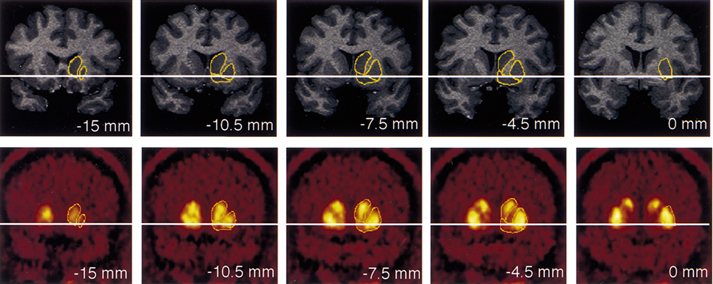
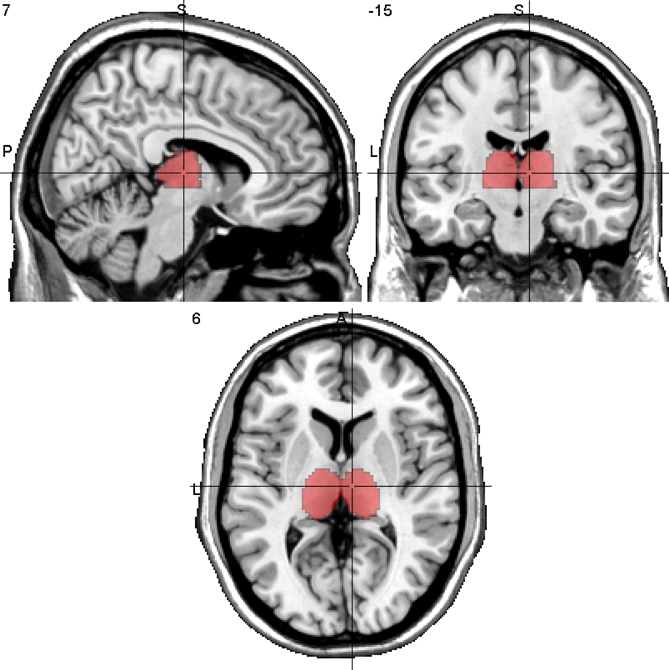
The Thalamus
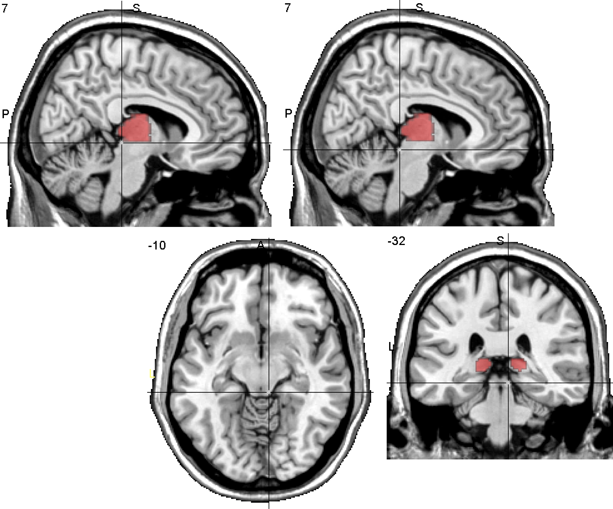
The Colliculi
Superior colliculus and inferior colliculus.
In the z direction, once you see the colliculi, you are not in the thalamus anymore
The upper left picture has crosshairs on the superior colliculus, the rest are centred on the inferior colliculus.
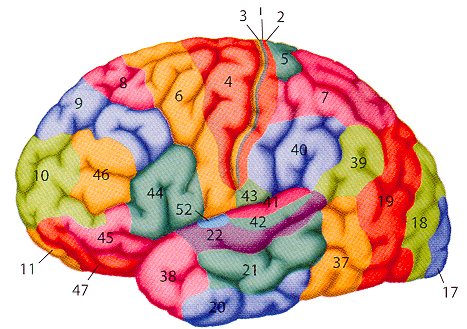
Brodmann Areas
In the cortex, Brodmann areas are often used in conjunction with anatomical lables to help specify an area.
|
1, 2, 3 = primary sensory cortex |
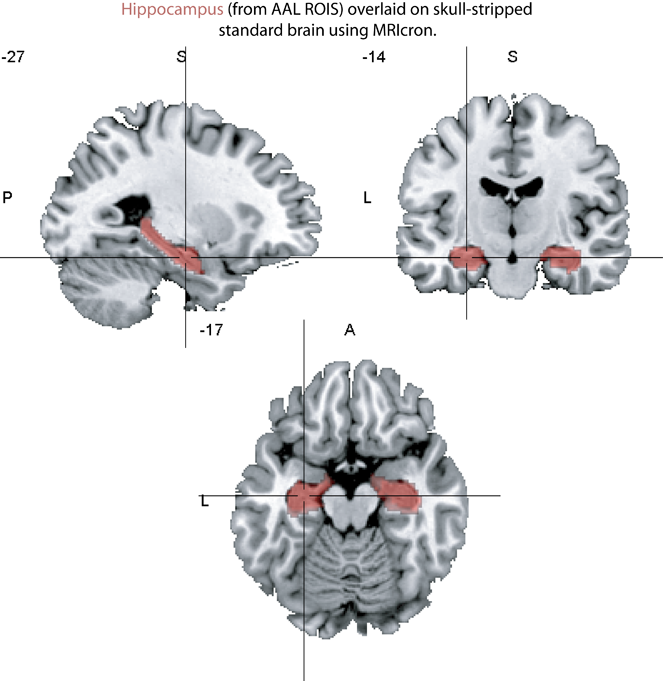
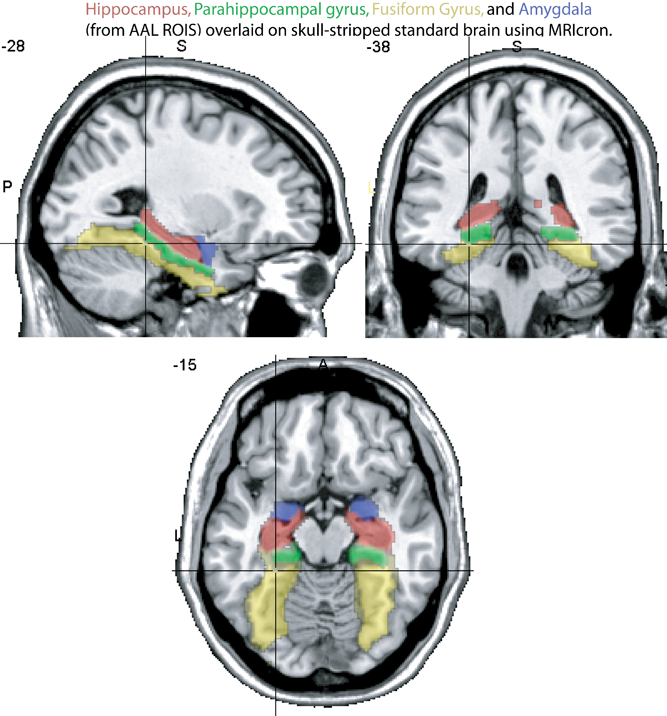
The medial temporal lobe
- hippocampus
- parahippocampal gyrus (roughly corresponds to parts of Brodmann areas 27, 28, 34, 35, 36)
- amygdala
- fusiform gyrus (roughly corresponds to parts of Brodmann areas 19, 37).
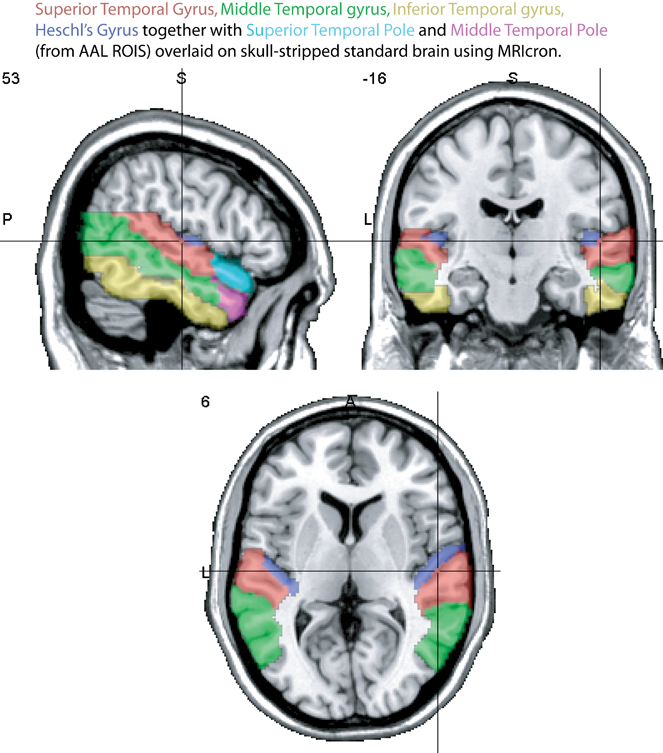
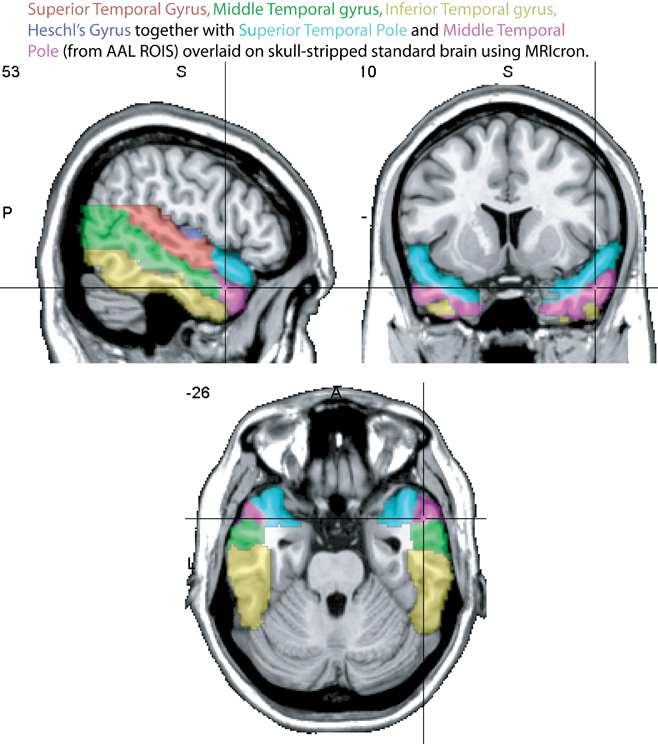
The lateral temporal lobe
- Inferior temporal gyrus (ITG)
- Middle temporal gyrus (MTG)
- Superior temporal gyrus (STG)
- Heschl's Gyrus (HG), also called transverse temporal gyrus. Contains primary auditory cortex
- Temporal poles
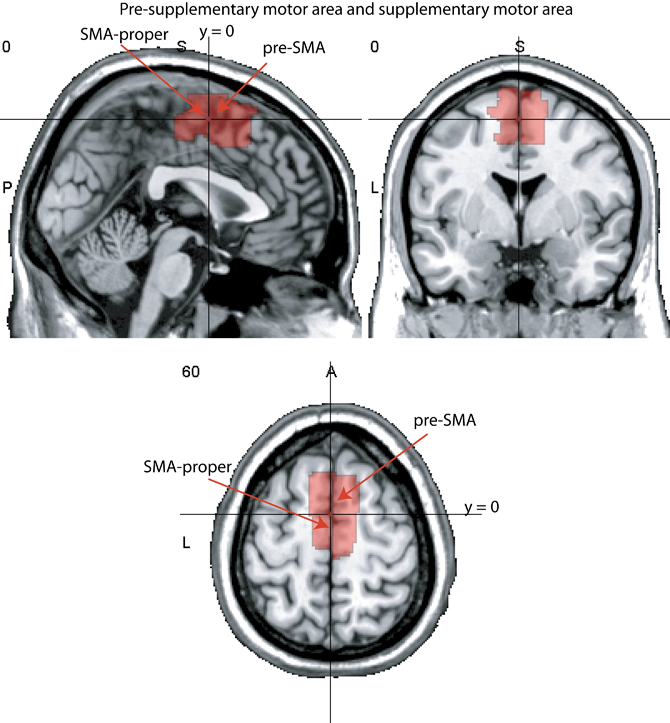
The supplementary and pre-supplementary motor areas
SMA and pre-SMA, medial Brodmann area 6
The dividing line between the pre-SMA and the SMA is often considered to be the plane of y = 0.
The anterior cingulate
Generally taken to have cognitive (red) and affective (blue) divisions.
Brodmann areas 24 and 32.
An excellent review (from which this figure was taken) is available here
The frontal lobe
- Superior (red), middle (blue), and medial (greeen on midline) frontal gyri.
- The inferior frontal gyrus is divided into pars opercularis (pink), pars triangularis (green), and pars orbitalis (yellow)
- Brodmann area 44 = Broca's area
- Brodmann area 45/47 = Ventrolateral prefronal cortex (VLPFC)
- Brodmann areas 9/46 = Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)

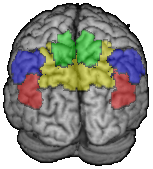
The parietal lobe
- Brodmann areas 5 (green) and 7 (yellow) = superior parietal lobule
- Brodmann areas 39 (red) and 40 (blue) = inferior parietal lobule
- Brodmann area 39 = angular gyrus
- Brodmann area 40 = supramarginal gyrus
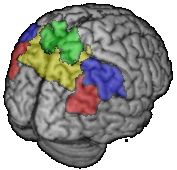
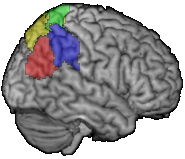
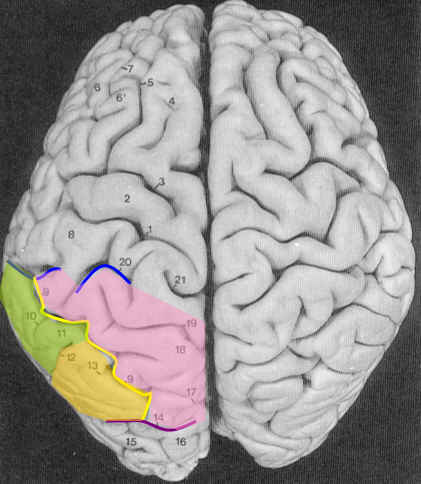
The Intraparietal sulcus divides superior and inferior lobules (yellow line on picture below)
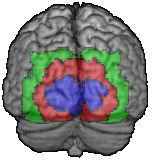
The occipital lobe
- Brodmann area 17 = primary visual cortex (blue)
- Brodmann 18 and 19 = secondary cortex (red and green)
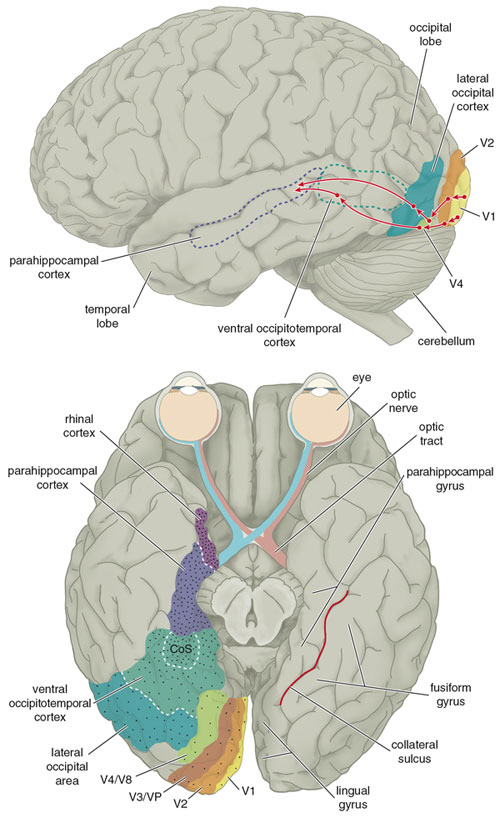
Structural and functional anatomy related to the visual system: a nice picture (from American Scientist magazine).
Links
The fMRI for Newbies site is filled with excellent information, including a page on functional anatomy.
Clickable MRI and modelled brain sections yoked together.
Click on Brain or detailed Brain.
Once you've loaded the brain, read the buttons at the top and experiment a bit to see how they work: 'remove model' and 'cross-reference' are handy places to start.
Site with clickable list of neuroanatomical terms, with pictures.
If you're desperate to know about sulci, this manual with pictures may be helpful.
A less comprehensive (and more comprehensible) sulci description.